|
|
Coastal and subcoastal saline swampCoastal and subcoastal saline swamp – FaunaClick on elements of the model or select from the tabs below
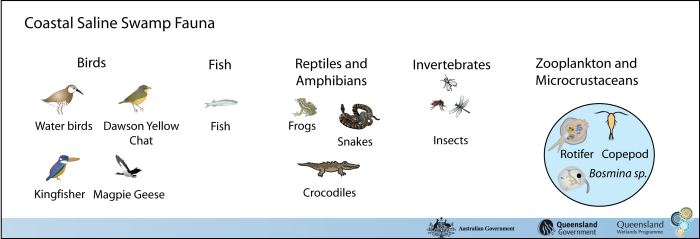
A range of birds use these areas for feeding and seasonal habitat. Ducks, cranes, black winged stilts, pelicans and magpie geese can all be found in this wetland habitat type, as can kingfishers (depending on the fish abundance). The critically endangered Dawson yellow chat (Epthianura crocea macgregori) can be found in some coastal areas of central Queensland, forming what is thought to be a distinct sub-population from the inland arid zone community. Crocodiles and acid frogs can be found in this wetland habitat type. During inundation, invertebrates drive the food web, and larger animals (such as freshwater crayfish and crabs) may occur. Where there is sufficient connectivity to streams, fish may occur. Though fish diversity tends to be low, coastal saline swamp habitats can be important nursery and feeding ground for barramundi and other fish species even if just for short periods of time. The depth of the waterbody is also a very important determinant for its usefulness as a fish habitat—deeper waters tend to have higher dissolved oxygen levels and provide more favourable habitats for fish for longer periods. A range of insects can be found in this wetland habitat type, including dragonflies, damselflies, mosquitoes and sandflies. Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal saline swamp – Fauna, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/palustrine/saline-swamp/fauna.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation