|
|
Alluvia—recharge process (inundation)Alluvia—recharge process (inundation)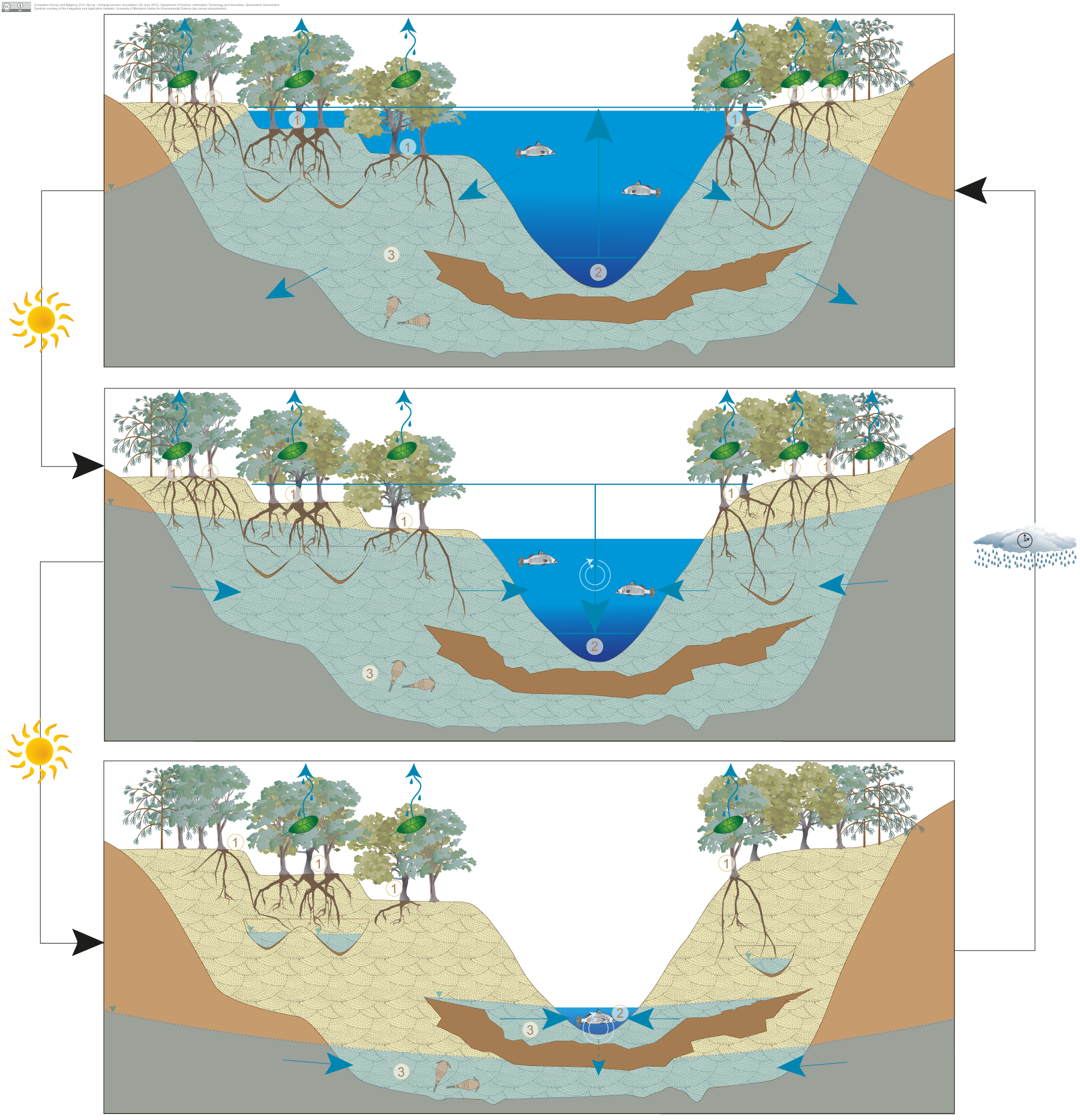
There are several processes that may occur individually or in conjunction with other processes to recharge groundwater in the alluvia: infiltration, discharge from surrounding water bearing geologies, and inundation. This conceptual model illustrates the recharge process of alluvial aquifers during inundation events (e.g. flooding).
Additional links
Last updated: 18 December 2015 This page should be cited as: Queensland Government, Queensland (2015) Alluvia—recharge process (inundation), WetlandInfo website, accessed 18 March 2024. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/groundwater-dependent/alluvia-recharge/ |

 — Department of Environment, Science and Innovation
— Department of Environment, Science and Innovation