|
|
Coastal sand masses (high dunes)Coastal sand masses (high dunes)High dunes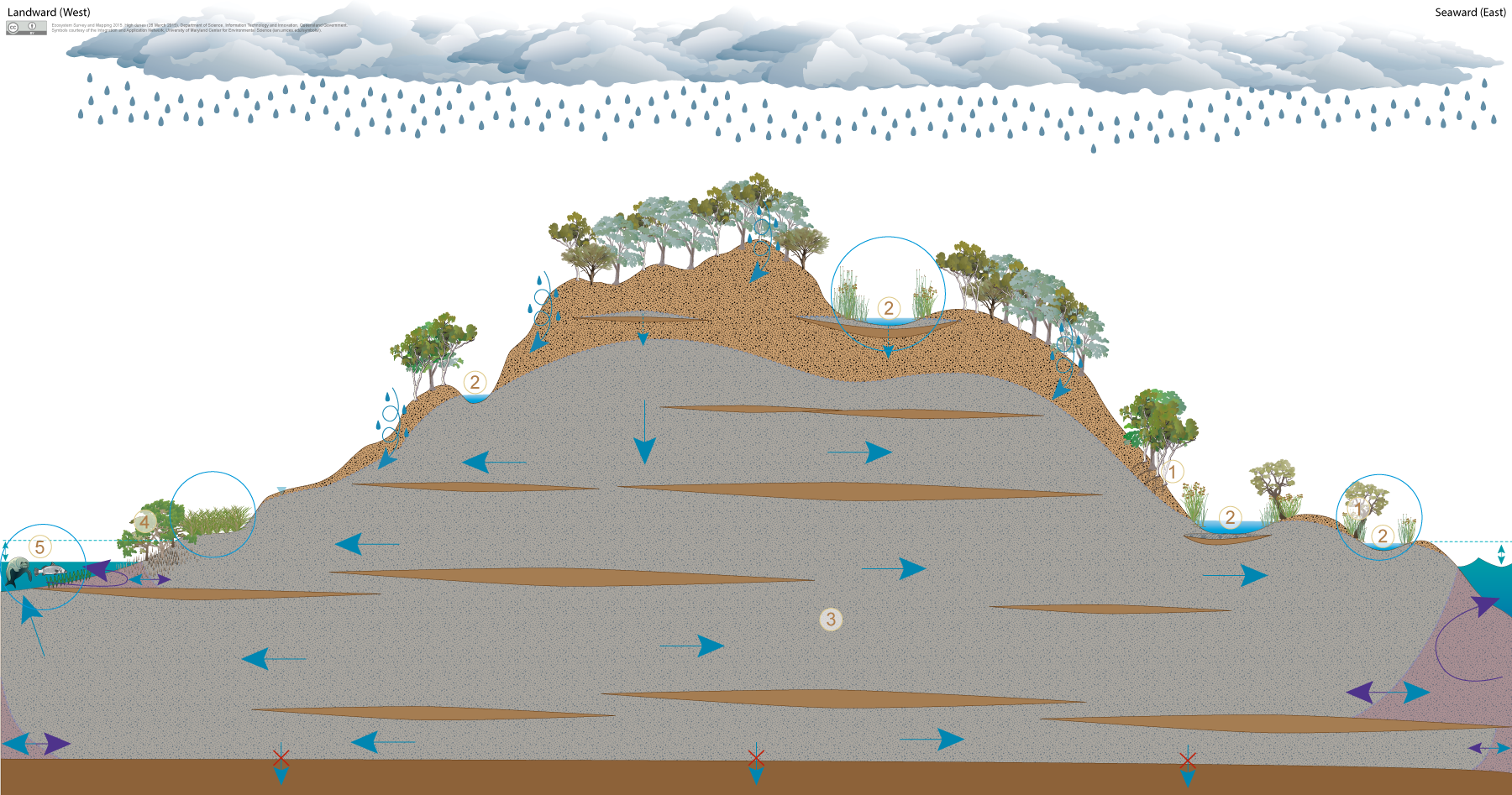 Click on elements of the model or select from the tabs below Coastal sand islands with high dunes usually contain one or more unconfined, unconsolidated sedimentary aquifers, where groundwater is stored and transmitted through inter-granular voids between sand particles. These unconsolidated sedimentary aquifers may be perched due to the presence of low permeability layers within the coastal sand mass (e.g. layers of coffee rock or beach rock). Examples of coastal sand islands with high dunes along the Queensland coast include Fraser, Moreton and North Stradbroke islands. A wide range of ecosystems may depend on groundwater in these unconsolidated sedimentary aquifers to support their plant and animal communities, ecological processes and delivery of ecosystem services.
Pictorial conceptual model PDF Additional linksLast updated: 18 December 2015 This page should be cited as: Queensland Government, Queensland (2015) Coastal sand masses (high dunes), WetlandInfo website, accessed 18 March 2024. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/groundwater-dependent/coastal-sand-mass-high-dunes/ |

 — Department of Environment, Science and Innovation
— Department of Environment, Science and Innovation