|
|
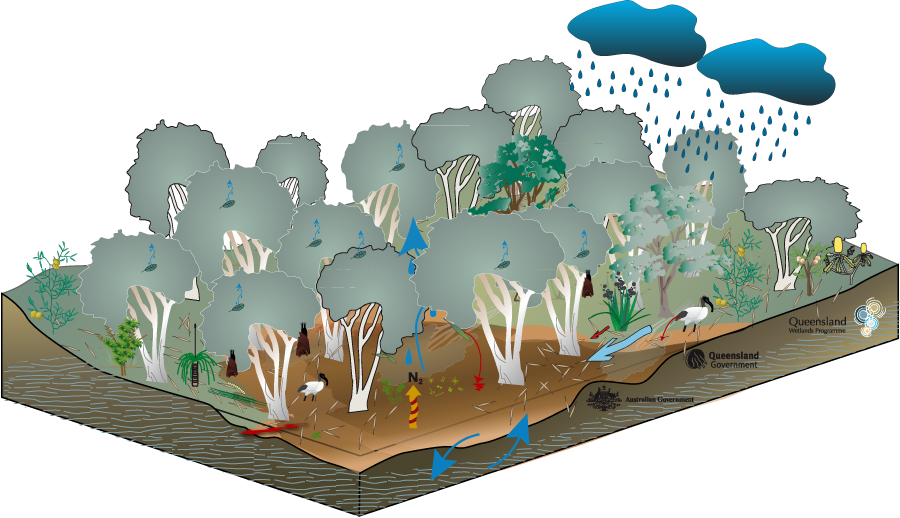
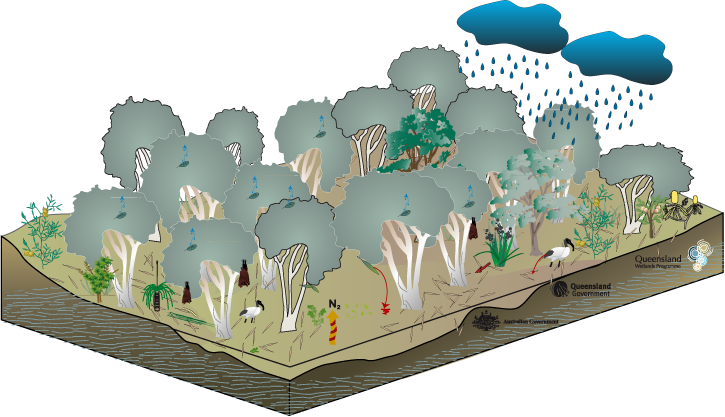
Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp.Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp. – FloraClick on elements of the model or select from the tabs below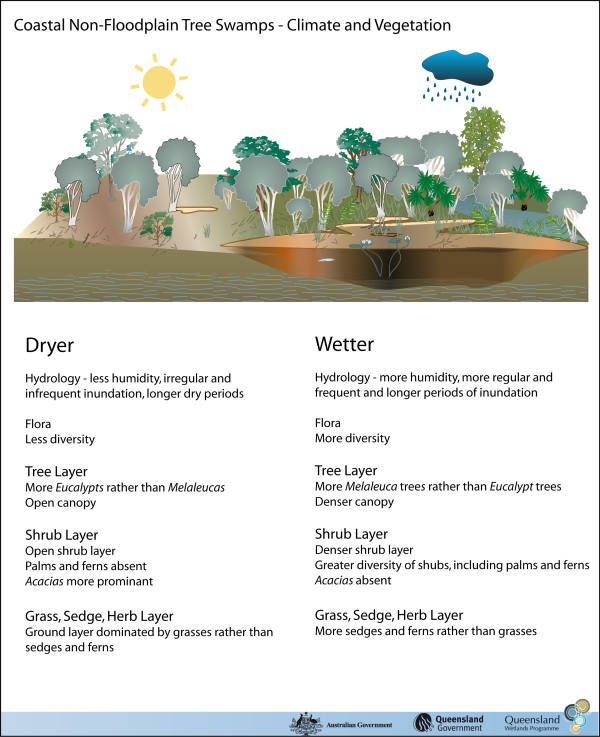 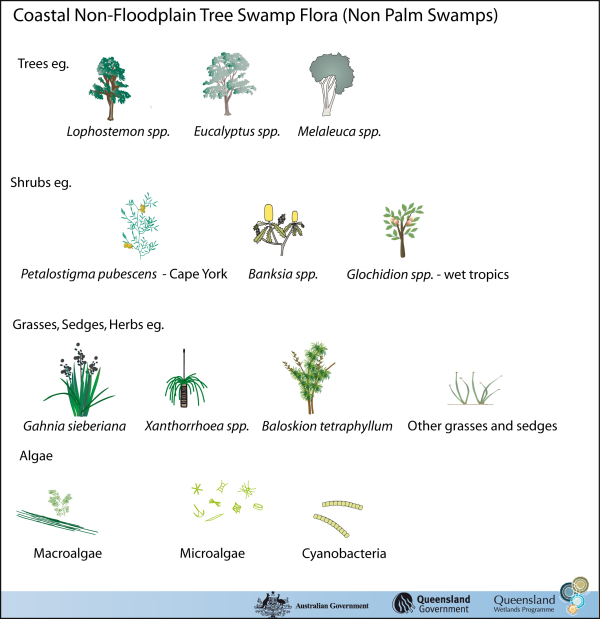  Melaleuca spp. can form almost pure stands and therefore floristic diversity is not necessarily a function of health in these systems. On flat land with good subsoil moisture Melaleuca spp. can occur alongside eucalypts in mixed tall open-forests. Other flora types (depending on the swamp’s positions within the landscape and its water regimes) include:
Different Melaleuca species are associated with slightly different soil types and water regimes conditions - flora diversity with climate pop out. Research suggests that the growth of Melaleuca quinquenervia can have a significant effect on the local soil chemistry and groundwater, increasing acidity (decreasing pH), changing redox potential and dissolved organic carbon levels. Though Melaleuca spp. trees cannot survive permanent inundation they do have adaptations such as fibrous or adventitious roots around their lower trunk that are thought to function as breathing roots, helping the tree to survive during long periods of submersion. The trees also have spreading root systems, providing stability during floods and prolonged water logging and most species are tolerant to a limited extent of both saline and brackish water. Tropical regional ecosystems3.3.32Melaleuca viridiflora ± M. saligna woodland in sinkholes and drainage depressions Occurs in sinkholes and drainage depressions. 3.3.50aMelaleuca viridiflora ± Petalostigma pubescens low open woodland on low plains Occurs on low-lying plains. 7.3.5aMelaleuca quinquenervia open-forest, woodland and shrubland, on poorly drained alluvial plains. Occurs on lowlands of the very wet and wet rainfall zone, on poorly drained peaty humic gley soils where the water table is near or above the ground for most of the year. Sub-tropical regional ecosystems12.2.7Melaleuca quinquenervia or M. viridiflora open forest to woodland on sand plains Occurs on Quaternary coastal dunes and seasonally waterlogged sand plains usually fringing drainage system behind beach ridge plains or on old dunes, swales and sandy coastal creek levees. 12.5.4aMelaleuca quinquenervia and or M. viridiflora woodland Occurs on complex of remnant Tertiary surfaces and Tertiary sedimentary rocks. Melaleuca spp. trees can flower all year round, providing an almost constant source of nectar and pollen, which is particularly important in winter for insects, birds and bats. Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp. – Flora, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/palustrine/non-floodplain-tree-swamp/flora.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation



