|
|
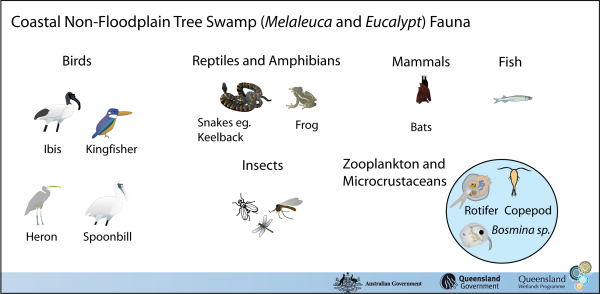
Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp.Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp. – FaunaClick on elements of the model or select from the tabs below
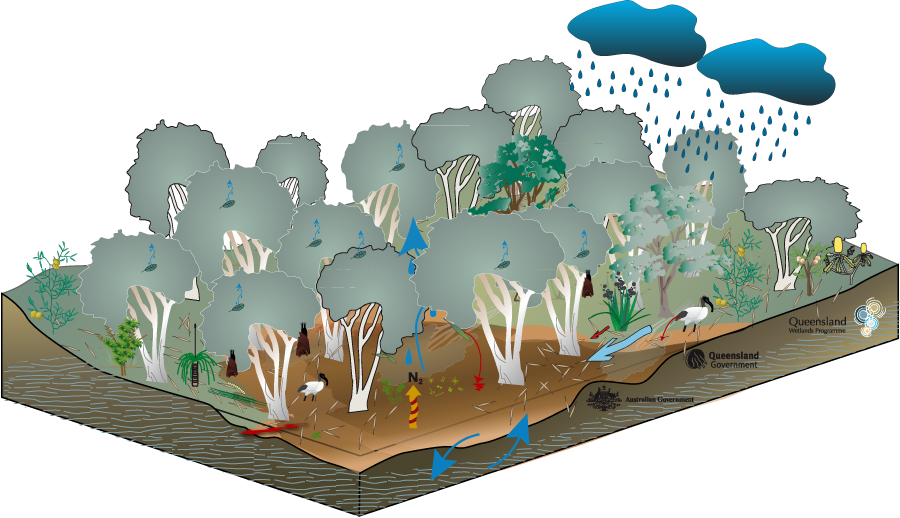
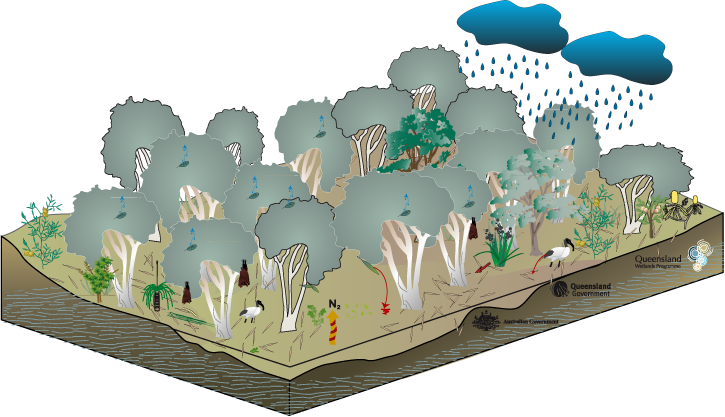
Melaleuca spp. trees can flower all year round, providing an almost constant source of nectar and pollen, which is particularly important in winter for insects, birds and bats. Bats are an important pollinator for Melaleuca spp. and hard wood trees. Relatively few fish species (approximately 3-4 species including tarpon) utilise these areas extensively, this is due to the typically low pH of the water and the ephemeral nature of these systems. The longer the wetland remains inundated the better habitat it provides for fish. Other animal species can also be found in tree swamps, including a range of bird species like spoonbills, ibis, kingfishers and herons, as well as a variety of insects and frogs. Reptiles that inhabit freshwater wetland habitats include the Red-bellied Black Snake (Pseudchis porphyriacus), Arafura File Snake (Acrochordus arafurae, which is largely aquatic) and the Freshwater Snake (Keelback Tropidonophis mairii). Zooplankton and microcrustaceans are microscopic aquatic fauna that graze on phytoplankton and detritus. Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain tree swamp—Melaleuca spp. and Eucalyptus spp. – Fauna, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/palustrine/non-floodplain-tree-swamp/fauna.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation