|
|
Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain sand lake—PerchedCoastal and subcoastal non-floodplain sand lake—Perched – Flora
Click on elements of the model or select from the tabs below
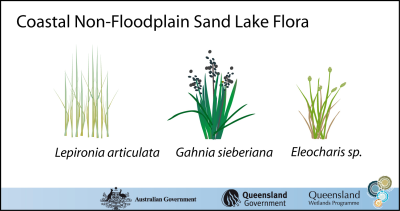
Oligotrophic (low nutrient) lakes are often surrounded and, if shallow, invaded by dense strands of sedges and rushes such as Lepironia articulata, Eleocharis spp., Baumea spp., Schoenus spp., Juncus spp. and Gahnia spp. The deeper areas of lakes are generally vegetation-free. Throughout Queensland, L. articulata is commonly associated with coastal dune lakes. However, species such as Baumea teretifolia, Eleocharis sphacelata, Leptocarpus tenax, common in south-east Queensland, are usually replaced with the species B. rubiginosa, E. brassi and Dapsilanthus ramosus in Cape York coastal dune lake areas. Coastal dune lakes can occur alongside a diverse range of wetland habitats and vegetation types including beaches, mangroves, salt flats, swamps, sedgelands, heathland and rainforest, depending on their exact location. Where lake levels fluctuate, vegetation surrounding the lake is highly water tolerant and may include species such as sundews (genus Drosera) and bladderworts (genus Utricularia). Some of the flora species associated with coastal dune lakes and their surrounding area include: Herbs
Sedges/Rushes
Trees/Shrubs
Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal non-floodplain sand lake—Perched – Flora, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/lacustrine/non-floodplain-perched-lake/flora.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation