|
|
Coastal and subcoastal floodplain grass, sedge, herb swampCoastal and subcoastal floodplain grass, sedge, herb swamp – HydrologyClick on elements of the model or select from the tabs below
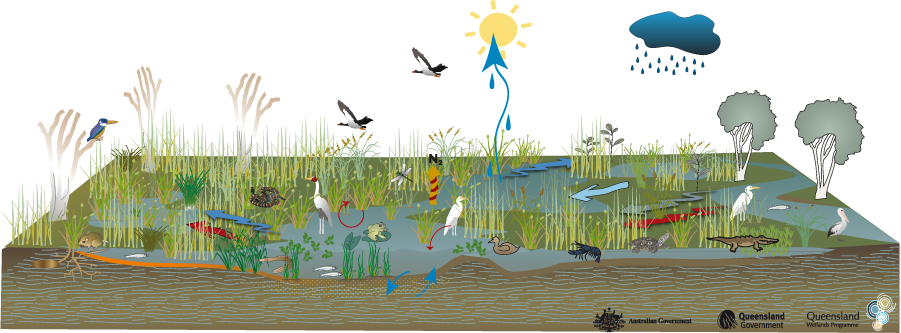
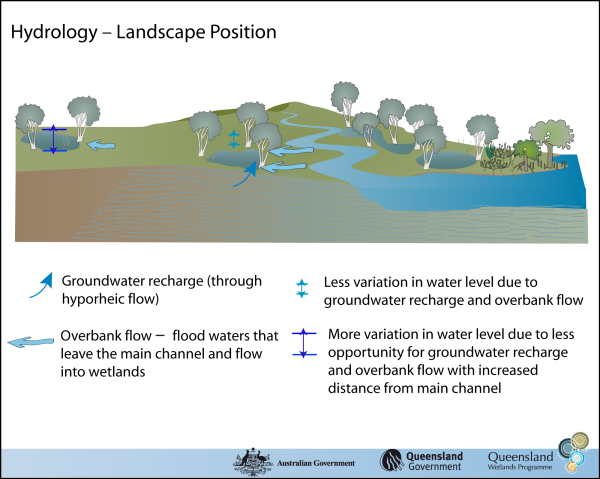
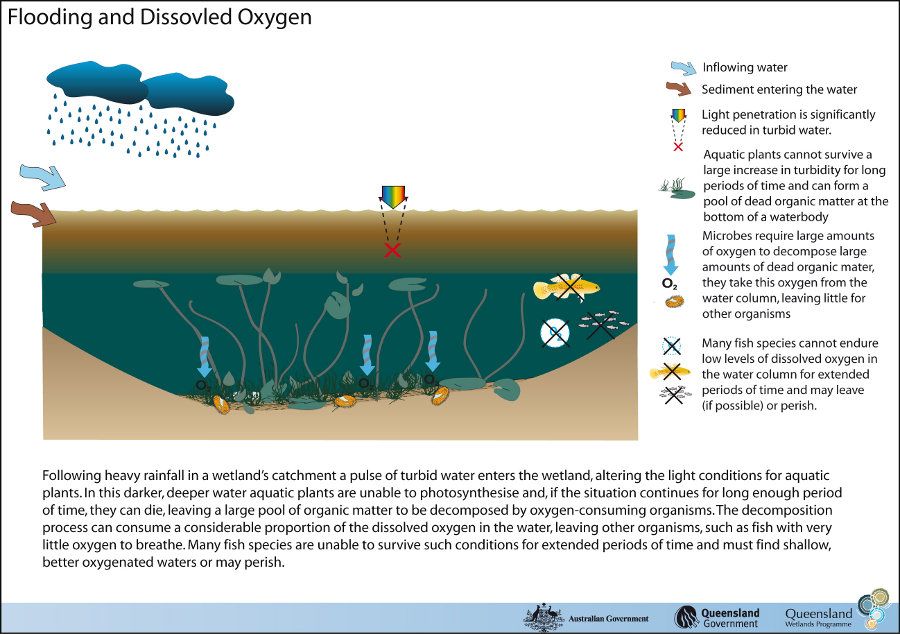
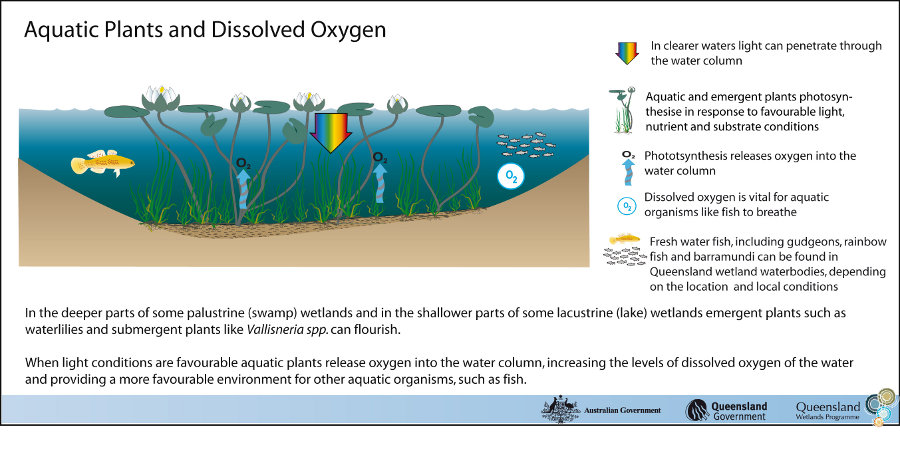
The hydrology of floodplain grass, sedge, herb swamp is related to a site’s local topography, substrate type and position within the catchment. Climatic factors (especially those related to rainfall) also play a significant role in the regularity, seasonality, duration and amount of water entering and leaving the wetland. Water InputsFloodplain wetlands can be flushed with water from overbank flow, streams leading directly to the site, sheet flow across the floodplain, rainfall, run-off from the local watershed, hyporheic flow and from sea water/groundwater interactions, or a combination of these sources. If groundwater table levels and substrate permeability permit, this can lead to more constant systems. This wetland habitat type can play a role in groundwater recharge/discharge. An important point to note is that hyporheic flow and groundwater flow tend to be clear (not turbid), compared to surface water flow. Water Outputs
Evaporation, transpiration and groundwater recharge can lead these systems to dry out, often completely (see dry model). Overbank floods move out onto the floodplain into wetlands and then may flow back to the stream or river channel, connecting the wetland habitat to other wetland habitats in the floodplain. Water may also flow out to the ocean via distributary channels, depending on topography. Other Hydrological InformationThis wetland habitat type is typically found on flat landscapes and therefore tends to experience a slow flow rate of water movement and only a limited capacity to retain any great depth of water. Inundation is usually temporary for all but the deepest parts of the wetland habitat, ranging from a few weeks each year during periods of heavy rain and flash flooding, to many months. In some cases, the wetlands may dry out only for a short period in the dry season or may remain wet in the innermost parts.
Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal floodplain grass, sedge, herb swamp – Hydrology, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/palustrine/floodplain-grass-sedge-herb-swamp/hydrology.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation