|
|
Coastal and subcoastal floodplain lakeCoastal and subcoastal floodplain lake – Flora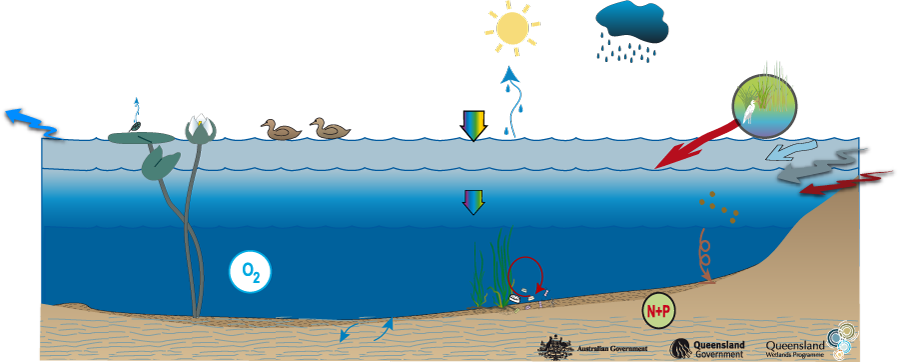 Click on elements of the model or select from the tabs below
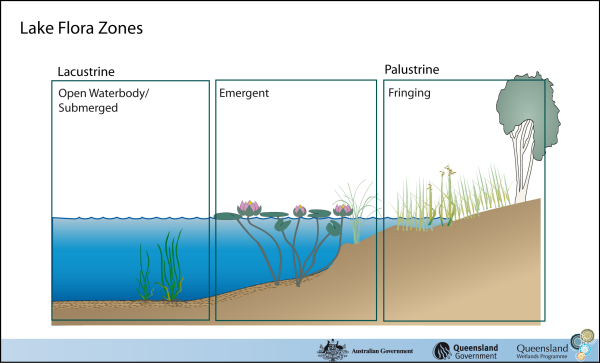
Lacustrine (lake) wetlands are often fringed by one or a number of palustrine (swamp) wetland habitat types and can go through a palustrine phase as they dry out. These palustrine wetland habitats are dealt with in other sections of this website. By definition, lakes lack substantial vegetation (to be defined as a lacustrine waterbody, there must be less than 30% vegetation cover). But they can have low levels of plant growth. The major types of plants are shown in the diagram to the right. Submerged plants are entirely aquatic. Emergent plants grow in lake sediment but breach the surface. They can form part of a lacustrine system if they cover less than 30% of the waterbody surface area. Otherwise they are classified as a palustrine habitat component. Fringing plants typically form the surrounding palustrine (swamp) wetland habitat component. Last updated: 22 March 2013 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2013) Coastal and subcoastal floodplain lake – Flora, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/lacustrine/coastal-floodplain-lake/flora.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation