|
|
High efficiency sediment basinsHigh efficiency sediment basins — Key considerationsSelect from the tabs below Requirement for effective treatment
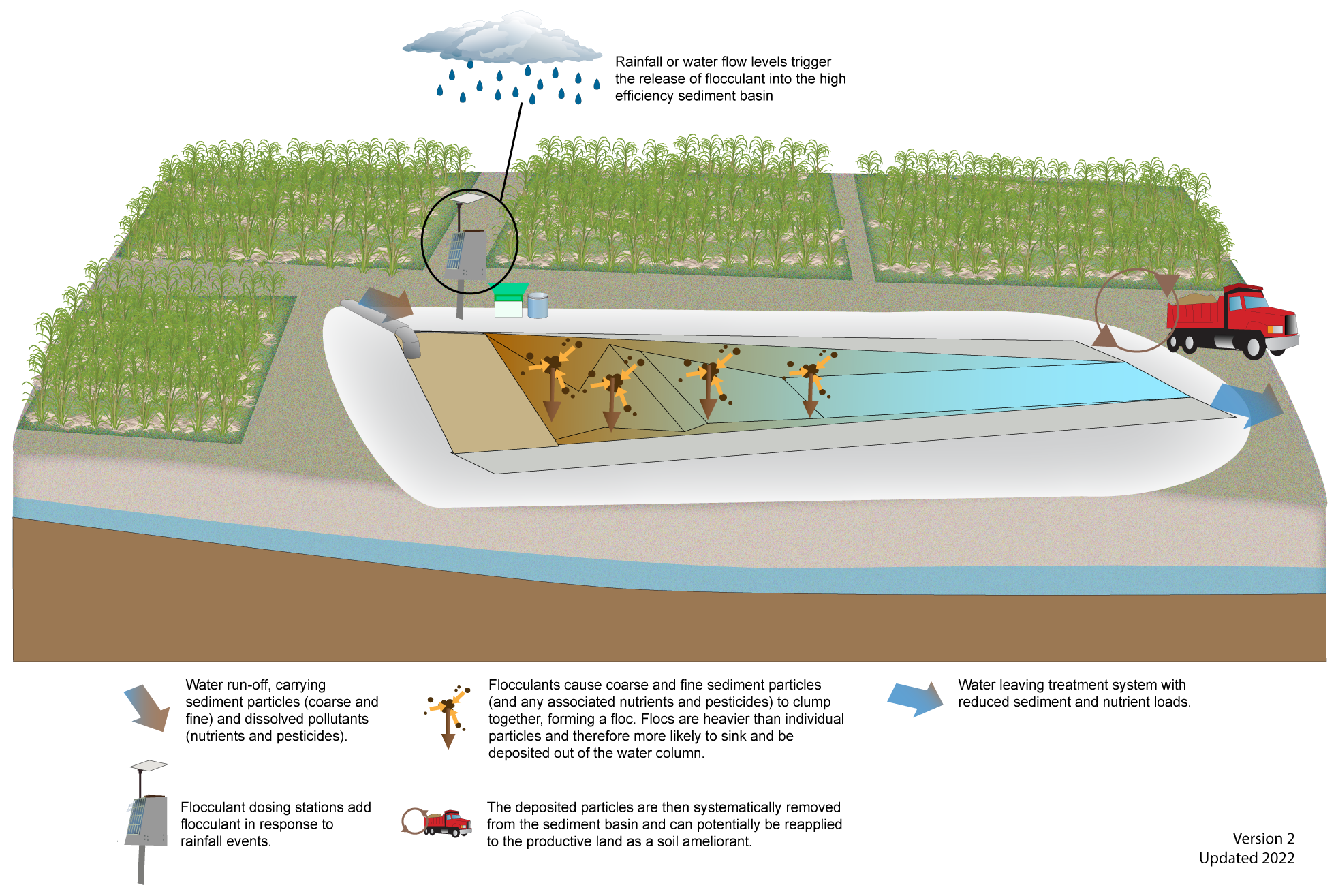
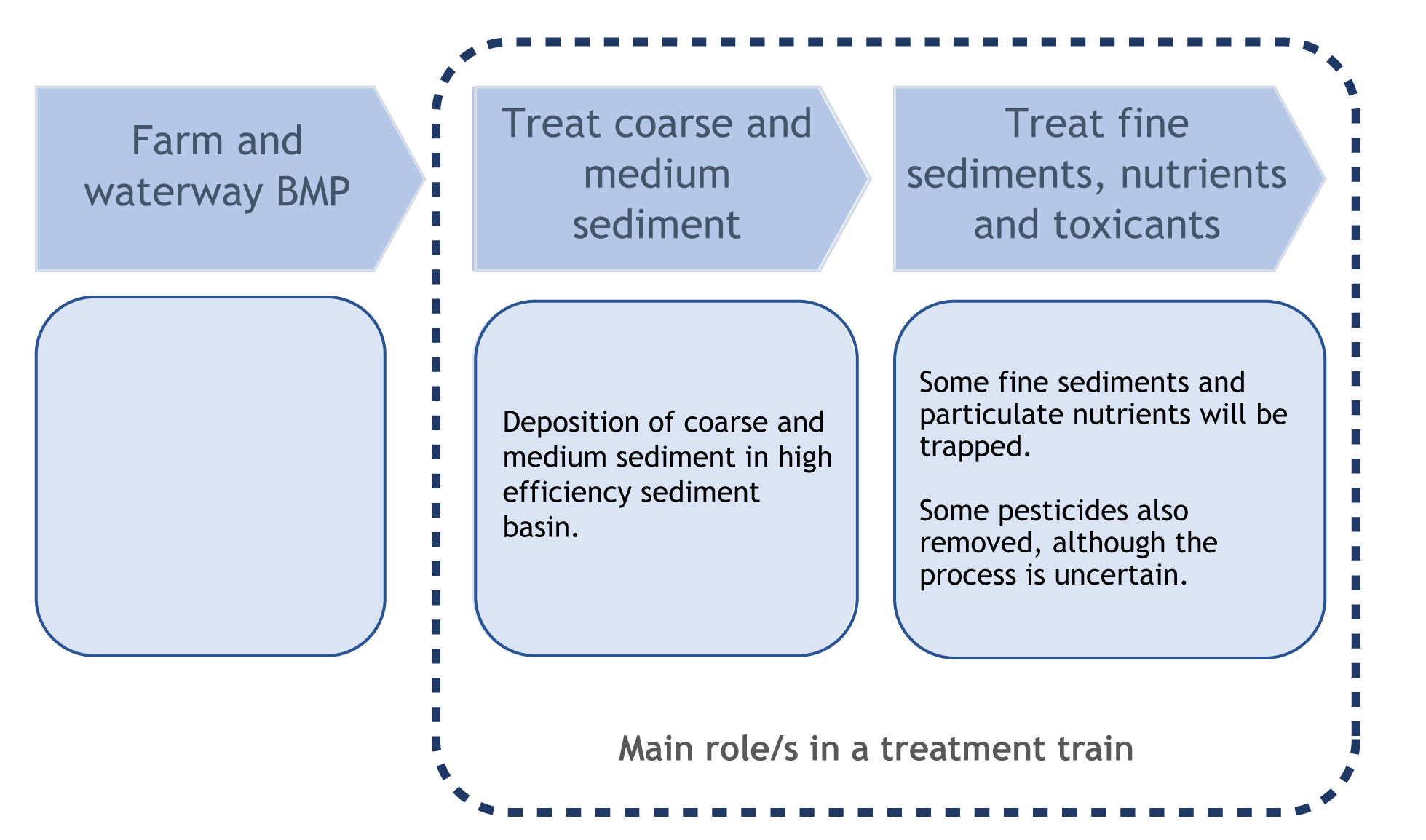
Suitability and limitationsHES basins, while not widespread in Queensland, have been used in a variety of agricultural industries to remove sediments and associated nutrients and pesticides[1]. Some trials have been conducted in Queensland[3]. HES basins have a small treatment area ‘footprint’ compared to vegetated treatment systems and more traditional forms of sediment basins. HES basins can be retrofitted to existing irrigation tailwater recycle pits or sediment basins/traps by adding an automatic coagulant dosing units to the primary inflow point(s)[3]. New permanent HES basins can be constructed at low points (e.g. farm drainage discharge points) or small HES basins can be constructed at drainage collection point(s) from land in fallow. HES basins do not rely on vegetation for enhanced sedimentation and are therefore less vulnerable to prolonged dry periods (such as experienced in the dry tropics region) compared to vegetated treatment systems such as constructed wetlands and bio-retention. Monitoring and modelling of an HES basin application in several Queensland locations shows high performance for suspended sediment and nutrient retention[3]. TSS load reduction: 80-90% TP load reduction: 70-90% TN load reduction: 45-65% HES basins are not a suitable treatment system in areas that regularly flood, where there is shallow groundwater or if the runoff or tailwater is saline as this increases the risk of deep drainage. The cost-effectiveness of high efficiency sediment basins in removing the target pollutant/s needs to be considered relative to other treatment structures. Refer to cost considerations for more information. Treatment processes
DisclaimerIn addition to the standard disclaimer located at the bottom of the page, please note the content presented is based on published knowledge of treatment systems. Many of the treatment systems described have not been trialled in different regions or land uses in Queensland. The information will be updated as new trials are conducted and monitored. If you have any additional information on treatment systems or suggestions for additional technologies please contact us using the feedback link at the bottom of this page. References
Last updated: 10 June 2022 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2022) High efficiency sediment basins — Key considerations , WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/management/treatment-systems/for-agriculture/treatment-sys-nav-page/high-efficiency-sediment-basins/design-summary.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation