|
|
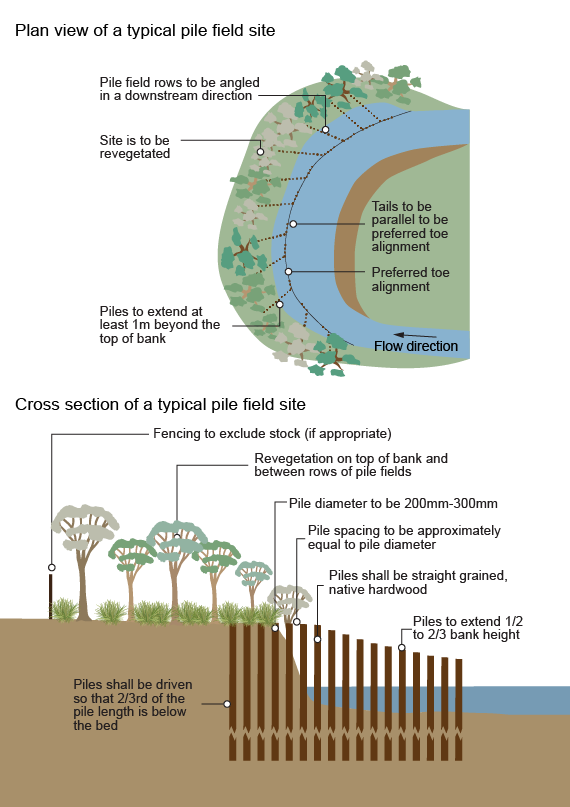
Alignment training (timber pile fields)Alignment training (timber pile fields) requires combined vegetation management and physical intervention. It involves the placement of wooden pile field structures to redirect high velocity flow away from a riverbank with the aim of reducing riverbank erosion and encouraging deposition at the bank toe. Revegetation is used to stabilise deposited sediments and increase hydraulic roughness, further reducing velocities at the bank. Alignment training (timber pile fields) requires combined vegetation management and physical intervention. This strategy should be focused on a long-term goal of vegetation establishment, eventually making the engineered structure redundant. Potential benefits from this intervention:
Potential negative implication from this intervention:
Intervention considerations:
Additional informationPublications: Department of Sustainability and Environment (DSE). 2007. Technical Guidelines for Waterway Management, Department of Sustainability and Environment, Victoria. Last updated: 9 June 2022 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2022) Alignment training (timber pile fields), WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/management/rehabilitation/rehab-process/step-4/intervention-options/alignment-training-mod.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation