|
|
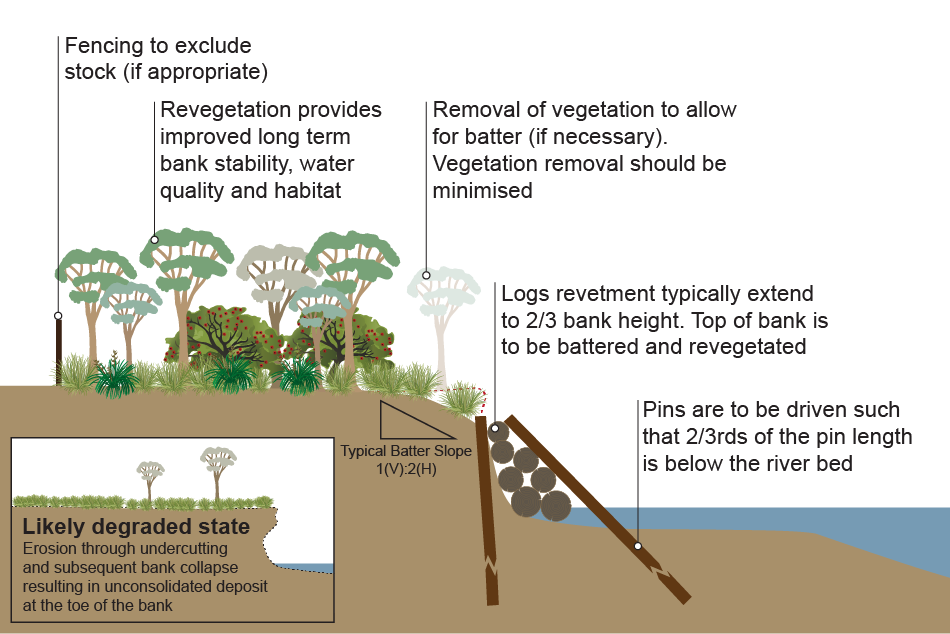
Timber revetmentTimber revetment (also known as log revetment) involves the placement of native hardwood timber on a riverbank with the objective of preventing bank erosion. Timber revetment typically extends into the bed of the river to deal with scour of the bed and is connected onto the bank with either timber piles or cables that are anchored at the top of the bank. A gravel filter layer or filter fabric can be placed under the timber to prevent flow permeating and eroding the bank material behind. This is a combined vegetation management and physical intervention approach. The engineered structure is needed to protect the toe of the bank by increasing its strength. This stops the retreat of the upper bank so that vegetation can establish. This strategy should be focused on vegetation establishment to achieve the objective, eventually making the engineered structure redundant. Compared to rock armouring, timber revetments take a longer time to fully establish bank protection. As such, this management intervention is often undertaken at sites with lower risks than those selected for rock armouring. Potential benefits from this intervention:
Potential negative implications from this intervention:
Intervention considerations:
Additional informationDepartment of Sustainability and Environment (DSE). 2007. Technical Guidelines for Waterway Management, Department of Sustainability and Environment, Victoria. Rutherfurd, I.D., Jerie, K. and Marsh, N. 2000. A Rehabilitation Manual for Australian Streams, Volumes 1 and 2. CRC for Catchment Hydrology and LWRRDC. Canberra. Last updated: 22 June 2022 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2022) Timber revetment, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/management/rehabilitation/rehab-process/step-4/intervention-options/timber-revetment-mod.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation