|
|
SewerageSewerage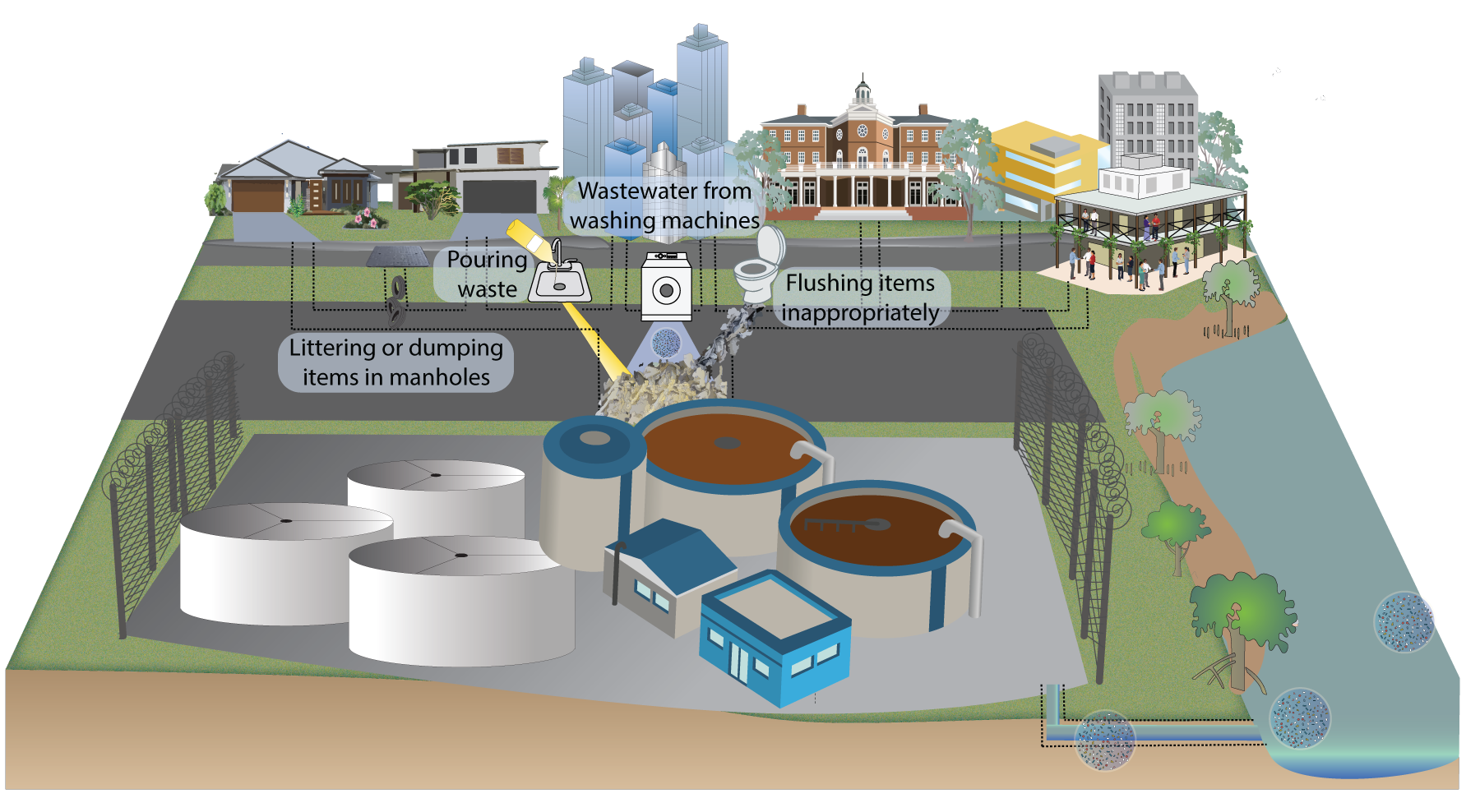 The sewerage system is generally taken to comprise:
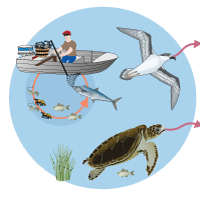
Sewage itself is not litter, however, given that treated effluent eventually goes into local water sources or the sea (after wastewater treatment), any residual items remaining in sewage can potentially become a type of litter. This litter may result from:
Although there is strict legislation covering sewage in Queensland, damage can still result from the improper disposal of materials down toilets, including plastic bags, sanitary items and chemicals. Small plastic items that are flushed into the sewerage system can get caught in pumps and create blockages, causing overflows and contamination. Illegal dumping down manholes can also damage sewerage infrastructure. As in so many other areas, the presence of microplastics and their flow through sewerage plants is only just being investigated. Microbeads (tiny pieces of plastic) are used as ingredients in many cosmetic products. Many microbeads are too small to be filtered out by wastewater plants and end up flowing into rivers and oceans[2][1]. Oils and fats in the sewerage system can combine to form ‘fatbergs’. These are difficult and expensive to manage, and can cause substantial damage to infrastructure, resulting in system closure and further expense. Waste pollution in the sewerage system moves through the environment via four pathways: References
Last updated: 22 April 2025 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2025) Sewerage, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/management/pressures/litter-illegal-dumping/sources/sewage/ |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation