|
|
Wetland hydrological modelsWetland models enable users to quantify and predict the performance of wetland systems. This is important to understand how best to use both natural and constructed treatment wetlands to improve water quality, and to support wetland rehabilitation[2].
Quick fact
Wetland hydrological models – Wetland contributing catchment modelSelect from the tabs below
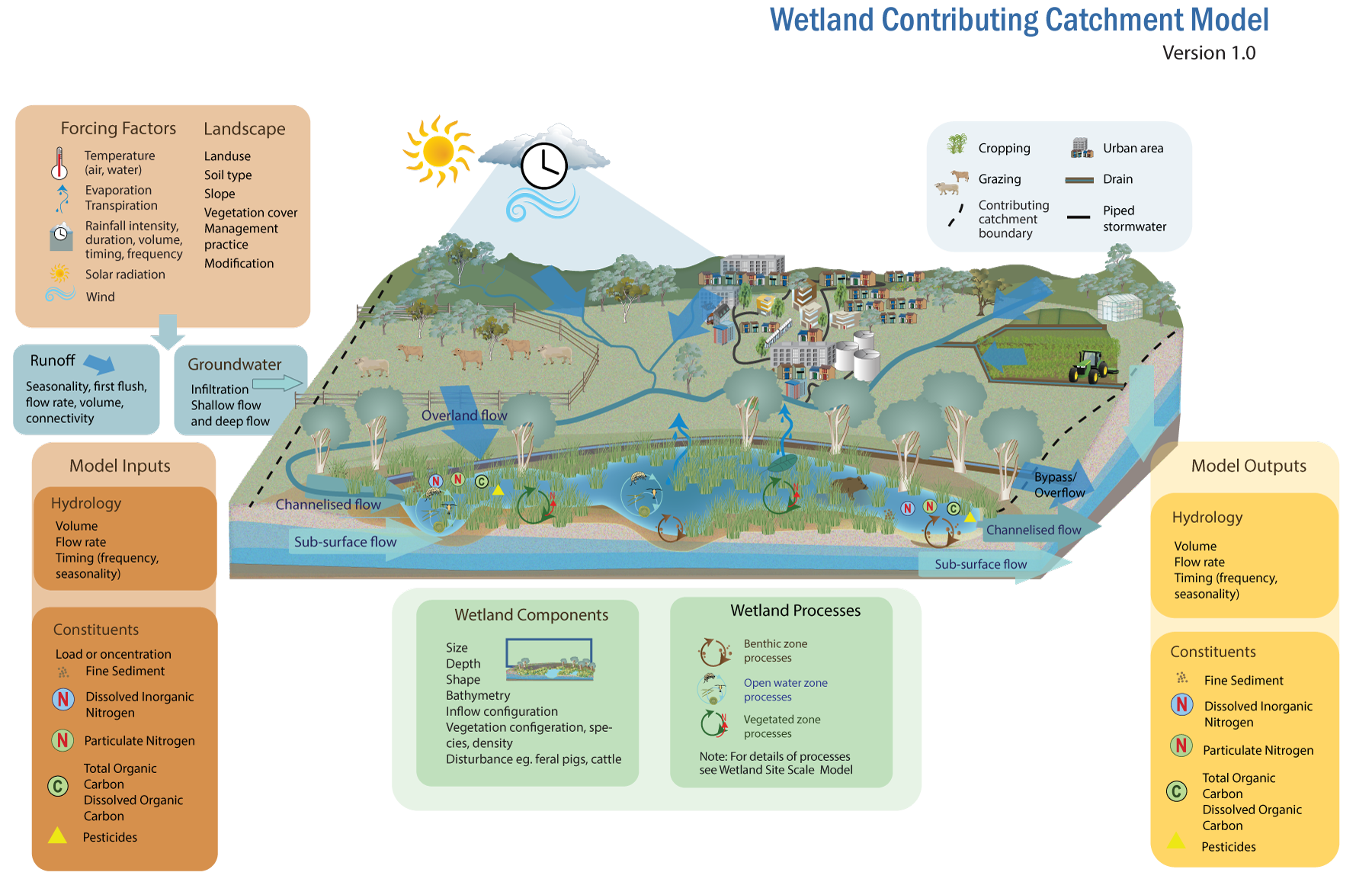
When modelling a wetland in terms of its local contributing catchment, a broader range of the hydrological and landscape factors (representing the contributing catchment of the wetland) may be incorporated to more accurately estimate the inputs to the wetland. The model boundary is the wetland’s interaction with the surrounding landscape – the local catchment area contributing water and constituents to the wetland. Forcing factors in terms of climatic variables act upon the landscape to generate runoff. The runoff in turn generates the model inputs in terms of surface runoff and groundwater. The climate forcing factors also influence the processes that occur in the wetland itself. Landscape components affect water inflows to wetlands depending on landuse (e.g. cropping, vegetation, urban impervious areas), soil type, geology (which influences percolation to groundwater), slope, vegetation cover, and management practices. Runoff flow rates and volumes from the wetland catchment as a result of rainfall are variable due to seasonality (e.g. wet and dry seasons), connectivity (e.g. the degree to which a wetland is connected to waterways), and landscape features, and may exhibit first flush characteristics in terms of pollutant concentrations and loads. References
Last updated: 31 May 2023 This page should be cited as: Department of Environment, Science and Innovation, Queensland (2023) Wetland hydrological models – Wetland contributing catchment model, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/facts-maps/modelling/wetlands-modelling/wetland-contributing-catchment-model.html |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation