|
|
Silkstone FormationSilkstone Formation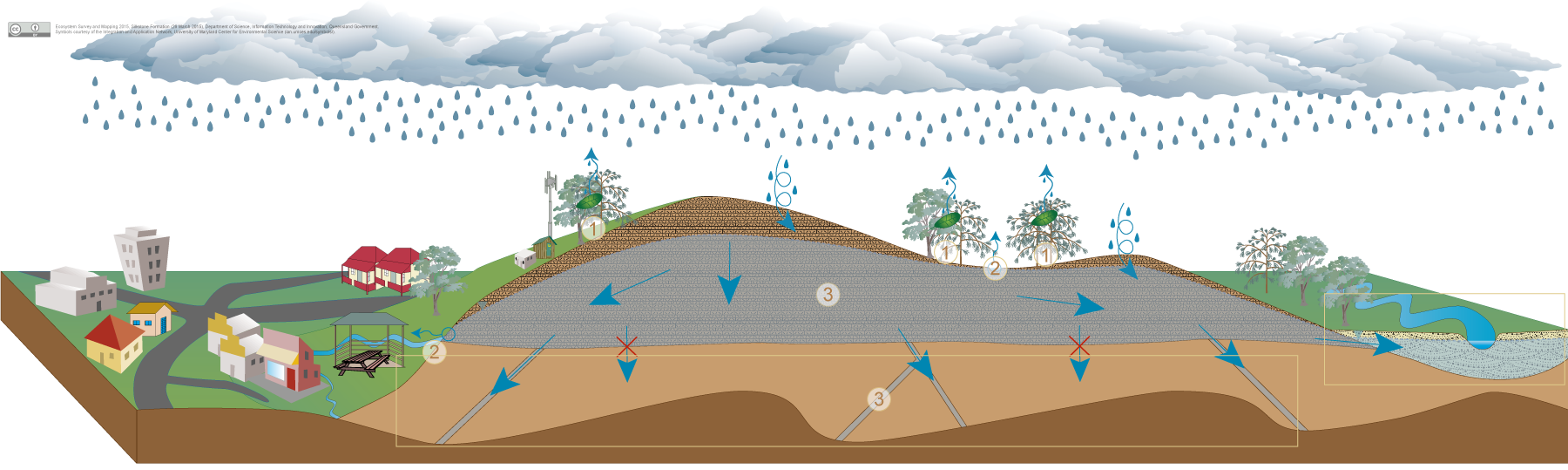
Click on elements of the model or select from the tabs below The Silkstone Formation is mostly comprised of limestone and basalt both of which may store and transmit groundwater through inter-granular pore space, fractures and weathered zones. Groundwater may discharge typically along foot slopes and drainage lines from these permeable rock aquifers. In South East Queensland the Silkstone Formation is restricted to the Ipswich and Redbank Plains areas and one other small occurrence of limestone occurs south of Peak Crossing. In the conceptual model above, the Silkstone Formation is shown as limestone with inter-bedded basalt flows throughout the Silkstone Formation. The permeable rock aquifers of the Silkstone Formation may provide a range of ecosystems with water required to support their plant and animal communities, ecological processes and delivery of ecosystem services.
This discharge of groundwater from permeable rock aquifers may also support nearby channels, alluvium and associated aquatic ecosystems through prolonged flow or groundwater recharge. Pictorial conceptual model PDF Additional links
Last updated: 18 December 2015 This page should be cited as: Queensland Government, Queensland (2015) Silkstone Formation, WetlandInfo website, accessed 8 May 2025. Available at: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/aquatic-ecosystems-natural/groundwater-dependent/silkstone-formation/ |

 — Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation
— Department of the Environment, Tourism, Science and Innovation

